Fatty liver is a condition of liver where fat is accumulated in the liver.
A healthy liver under normal circumstances contains little or no fat at all.
Fatty liver disease is a broad disease with spectrum of wide range of liver diseases.
What’s Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases
NAFLD
Fatty Liver Disease
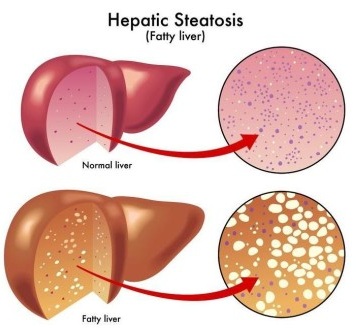
Types of Fatty liver disease
- Alcoholic fatty liver
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Alcoholic Fatty liver Disease
Alcoholic Fatty Liver disease is seen in people who consume alcohol heavily. The condition is reversible if the person stops drinking alcohol and if they continue to drink it progresses to serious conditions like liver cirrhosis and liver failure.
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) as the name suggests is type of fatty liver disease with fat accumulation in liver that is not associated with significant consumption of alcohol, or other competing reasons for fatty liver and other co –existing liver diseases.
Spectrum of NAFLD
Simple Fatty Liver
Simple fatty liver or NAFLD is a condition where only fat is accumulated in the liver cells
Non-alcoholic steatohepatosis (NASH)
NASH is more severe form of NAFLD, where along with fat accumulation there is inflammation and cell death in the liver with considerable scar (fibrous/hard) tissue formation
.
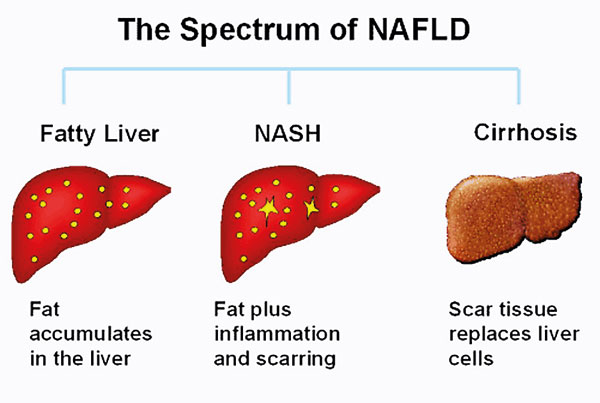
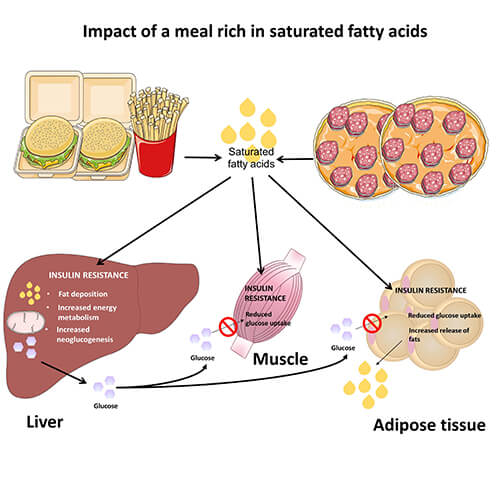
Why does fat gets accumulated in the liver?
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is an indicator of an abnormality of metabolism (chemical process) within the liver.
The liver is involved in metabolism of fat like absorption of fat from the food we eat or from the blood and transporting fat to other parts of the body. So overall the fat in the body is managed or handled by the liver cells, and in NAFLD the effective handling of the fat by liver is disturbed.
Where does the excess fat accumulated in liver come from?
The fat that is deposited in the liver comes from
- Fat from food
- Free fatty acids from blood convert into fat in liver
- Liver itself produces fat
- Reduced transportation of fat from liver
- Reduced disposal of fat from liver
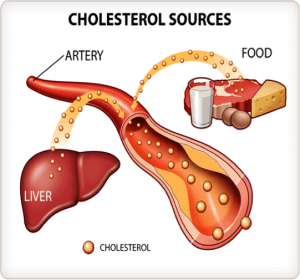
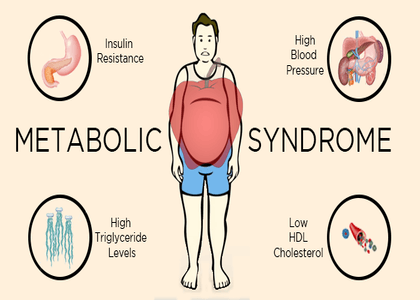
What causes the metabolic disturbances in liver?
It is not yet fully established what exactly causes NAFLD/NASH but studies have found that both NAFLD and NASH are linked to underlying conditions like obesity, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, high levels of cholesterol, type 2 diabetes and certain medications.
What are signs and symptoms of NAFLD?
There are no symptoms for NAFLD and so is called a silent disease. In majority of the cases it is accidentally identified during blood tests or imaging tests like ultrasonography and fibroscan.
Why is it important to consider NAFLD?
It is very important to take NAFLD seriously because NAFLD
- Is a sign of an underlying cause that NAFLD closely shares like type 2 diabetes
- Has proven outcomes like type 2 diabetes, fibrosis of liver, liver cancer, heart diseases and early death due to liver and heart complications
NASH – Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis
NASH is the most severe form of NAFLD characterized by abnormal accumulation of fat in the liver along with inflammation (hepatitis) and liver cell damage or cell death (ballooning). NASH can progress rapidly in many to fibrosis, cirrhosis and finally to liver failure or liver cancer .
NASH a silent killer
NASH generally doesn’t show any symptoms and is considered to be silent killer due to the very reason, but on few occasions some people with more severe fibrosis or cirrhosis may experience
- A dull or aching pain over the upper right side of the stomach (lower right side of the ribs)
- Extreme tiredness, weakness
- Loss of weight and loss of appetite
Outcomes of NASH
The progressive nature of NASH has shown to contribute to the following complications
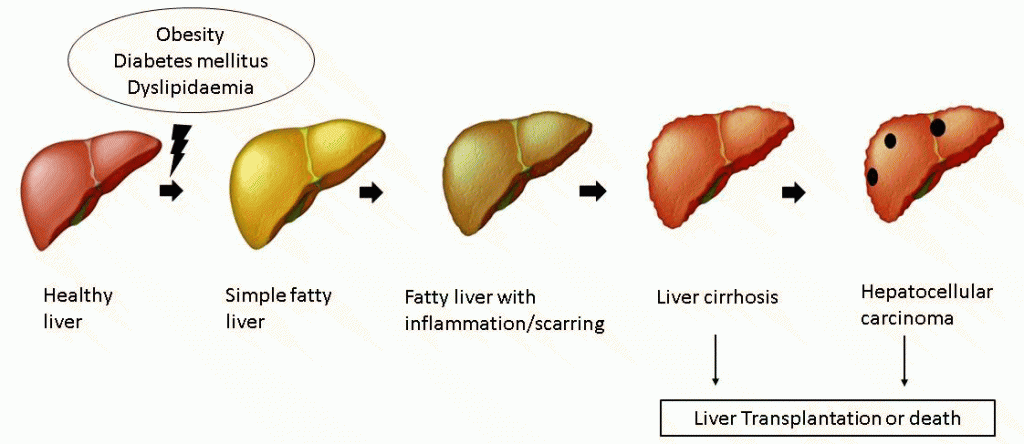
Liver Fibrosis –accumulation of fat over long period damages the liver cells, as a result the body reacts to injury by natural healing process with formation of fibrous (scar/hard) tissue replacing the damaged tissue. The scar tissue causes insufficient blood supply to the liver. Studies have shown that 37 – 41% of people with NASH have developed fibrosis of their liver over time
Liver Cirrhosis – Excessive fibrous tissue (scar tissue) over time progress to cirrhosis of the liver. In cirrhosis a much stronger scar tissue (stage- 4 fibrosis) is formed which puts the patient in a greater danger of loss of liver function (end-stage-liver disease). Studies have also shown that 5% of people with NASH went on to develop cirrhosis of liver.
Liver Failure – In patients with NASH related cirrhosis the liver may eventually fail to function due to extensive damage of the liver by cirrhosis, thus requiring a liver transplant to survive
Heart diseases – Both NAFLD and NASH can cause heart related diseases and it is shown in a study that 13% of people with NASH had higher chances of death from heart diseases
Liver Cancer – Both NAFLD and NASH are known to cause hepatocellular carcinoma, a type of liver cancer
Other complications – It is a known fact that type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome go hand in hand, so people with NASH may develop type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome
Increased chances of death – People with NASH have higher chances of death from liver and heart complications compared to general population without any liver diseases
Reference:
- Chalasani, N. , Younossi, Z. , Lavine, J. E., Charlton, M. , Cusi, K. , Rinella, M. , Harrison, S. A., Brunt, E. M. and Sanyal, A. J. (2018), The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology, 67: 328-357. doi:10.1002/hep.29367
-
Duseja A et al. (2015). Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Metabolic Syndrome, J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2015 Mar;5(1):51-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2015.02.006. Epub 2015 Mar 6
