What is NAFLD?
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease refers to the umbrella term that consists of liver ailments. As the name goes, NAFLD (Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) refers to fatty liver resulting from alcohol consumption or obesity. Many other factors contribute to the development of the liver fat. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) can happen at a later stage of NAFLD, whose characteristics are inflammation in the liver, liver scaring and in worst cases, cirrhosis and liver cancer.
We can identify the disease with some symptoms –
- Fatigue
- Chronic pain in the abdominal area
- Enlarged spleen
- Redness around the palms and hands
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes
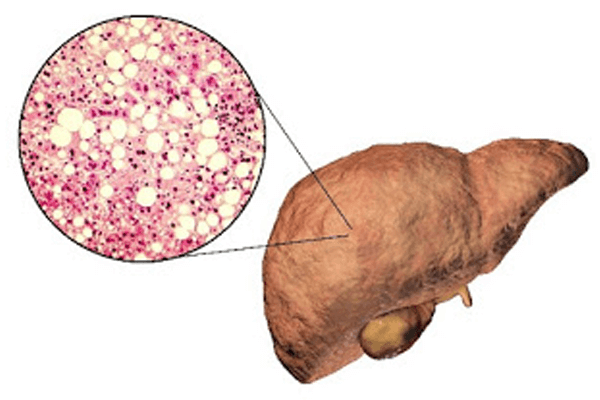
Although it is commonly considered that fatty liver occurs due to alcohol consumption, the surprising fact is that there are more to the disease than we can think. Among the factors which lead to the development of fatty liver disease are – obesity, insulin resistance, improper food habits, high blood sugar (hyperglycaemia) indicating type 2 diabetes and also high level of fat in the blood.
Blood lipids – ‘Blood lipids’ is a term used for all the fatty substances found in the blood. Cholesterol and triglycerides can be tagged as blood lipids. People having too much cholesterol in their blood are at high risk of heart diseases.
Cholesterol, the fatty substances which are mainly made in the body when the liver breaks down the saturated fats in food.
Triglycerides are another type of fat found in the blood which are contributed by food items. Drinking too much alcohol, sugary drinks, eating meat or too other much fat-based foods can cause calories to settle down in the body. The liver breaks down into triglycerides which are stored in our body as fat and are used as energy.
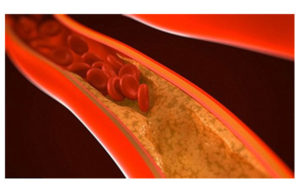 Having high level of fat in your blood can cause fat to deposit in the blood vessels including the coronary arteries that could further cause narrowing or hardening of the arteries and lead to various heart diseases.
Having high level of fat in your blood can cause fat to deposit in the blood vessels including the coronary arteries that could further cause narrowing or hardening of the arteries and lead to various heart diseases.
Although, NAFLD can get to a stage where it is difficult to cope with it, we can take up some preventions that will clear the effect by tremendous amount. As one of the main factors of fatty liver is obesity, one can shift their unhealthy diet to a healthy one. Consuming fruits and veggies and avoiding fat packed food items can really help combat Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Foods to avoid in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease are sugary drinks, fat-based food items, high calorie foods, alcohol, salt, white bread, rice, pasta, red meat etc. Obesity being the major factor contributing to the disease, one can invest time in exercising. Daily workout and physical exercise can immensely help in eroding the fat in liver and prevent fatty liver or NAFLD to occur. These workouts may include cycling, running, jogging, walking, yoga, warm up exercises etc.
What are the causes of NAFLD?
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, NAFLD, is an acute liver condition where reasons like obesity, type-2 diabetes, high blood pressure, insulin resistance and consumption of junk food and sugar-based beverages trigger the disease. In fact, obesity makes up one of the major causes of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.
NAFLD, if left untreated, can lead to Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) further leading to critical complications like cirrhosis, scarring, and fibrosis. These complications, if left without attention, can lead to liver failure and death.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of NAFLD
 Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Symptoms, as said before, include enlarged spleen, excess belly fat, high blood pressure, fatigue, pain in the abdomen, high levels of triglyceride that shows that the liver is getting weak and fat is accumulating in it. The liver, when weakened with fat, can’t take up the sugar while responding to the hormone insulin, and makes it insulin resistance which is not a good sign for the body.
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Symptoms, as said before, include enlarged spleen, excess belly fat, high blood pressure, fatigue, pain in the abdomen, high levels of triglyceride that shows that the liver is getting weak and fat is accumulating in it. The liver, when weakened with fat, can’t take up the sugar while responding to the hormone insulin, and makes it insulin resistance which is not a good sign for the body.
Because NAFLD shows no symptoms in most of the cases, it comes to medical attention only when tests are done for other reasons which points out any liver problem. This happens if your liver looks fatty after an ultrasound test or if you have an unusual liver enzyme test.
There are few blood tests that can be performed to diagnose and determine fatty liver disease severity including:
- Complete blood count
- Liver enzyme and liver function tests
- Tests for chronic viral hepatitis (hepatitis A, hepatitis C and others)
- Celiac disease screening test
- Fasting blood sugar
- Haemoglobin A1C, which shows the stability of your blood sugar
- Lipid profile, which measures blood fats, such as cholesterol and triglycerides
Imaging procedures conducted to find NAFLD include:
- Abdominal ultrasound, which is often used in the initial test when liver disease is suspected.
- Computerized tomography (CT) scanning or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdomen. These techniques lack the ability to distinguish NASH from NAFLD, but still may be used.
- Transient elastography, an advanced form of ultrasound that measures the stiffness of your liver. Liver stiffness are symptoms of fibrosis or scarring.
- Magnetic resonance elastography, works by combining MRI imaging with sound waves to create a visual map (elastogram) showing the stiffness of body tissues.
Liver tissue examination-
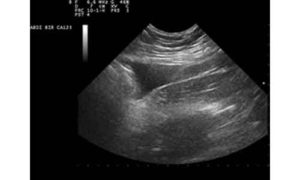 If other tests are not able to detect the fatty liver, your doctor may recommend a procedure to remove a sample of tissue from your liver (liver biopsy). The tissue sample is examined in a laboratory to look for signs of inflammation and scarring. A liver biopsy can be uneasy, and it does have small risks that your doctor will review with you in detail. This procedure is performed through a needle insertion through the abdominal wall and into the liver.
If other tests are not able to detect the fatty liver, your doctor may recommend a procedure to remove a sample of tissue from your liver (liver biopsy). The tissue sample is examined in a laboratory to look for signs of inflammation and scarring. A liver biopsy can be uneasy, and it does have small risks that your doctor will review with you in detail. This procedure is performed through a needle insertion through the abdominal wall and into the liver.
Treatment for NAFLD?
There are few easy steps for the curing of NAFLD or NASH, or Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Treatment.
 Weight loss is one of the ways to fight with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in India, dietary modification also helps fight with the fatal disease. Reducing calorie intake and losing weight to a significant level can help decrease the level of fat in the liver. Consuming foods such as olive oil, avocados, and various nuts helps in reducing liver fat. Also, whey protein helps lower the liver enzymes and help cope with NAFLD. Sipping on green tea also decreases liver fat as it contains the antioxidant – catechins, which helps reduce the inflammation or scarring in patients with NAFLD. Consuming soluble fibre can also be considered as Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Treatment as it helps to decrease liver fat too.
Weight loss is one of the ways to fight with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in India, dietary modification also helps fight with the fatal disease. Reducing calorie intake and losing weight to a significant level can help decrease the level of fat in the liver. Consuming foods such as olive oil, avocados, and various nuts helps in reducing liver fat. Also, whey protein helps lower the liver enzymes and help cope with NAFLD. Sipping on green tea also decreases liver fat as it contains the antioxidant – catechins, which helps reduce the inflammation or scarring in patients with NAFLD. Consuming soluble fibre can also be considered as Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Treatment as it helps to decrease liver fat too.
In addition to this, working on the muscles is recommended to reduce the fat stored in the liver cells and decrease the risk of NAFLD. 30-60 minutes of workout shows huge results and helps in a reduction of the risk associated with fatty liver. A regular workout can get the muscles working and lose the fat that could lead it to settle in the liver. Physical Exercise for NAFLD is highly recommended as it is one of the most natural ways to discard fat from the body.
NAFLD or NASH in India is becoming the most common liver disease with a worldwide prevalence of 25%. India is evolving into the diabetic capital of the world and non alcoholic fatty liver disease in India is emerging as an important cause of liver disease. Epidemiological studies suggest the prevalence of NAFLD or NASH in India to be around 9-32% within general Indian population. Even people with a lean physique may be metabolically obese.
Considering the ongoing obesity epidemic that can begin since childhood, the risk of diabetes, and other factors, the prevalence of NAFLD or NASH along with the percentage of those with advanced liver disease is said to continue to increase. NAFLD patients with symptoms of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis or NASH and advanced fibrosis are at recorded increased risk of adverse outcomes, including overall mortality, and liver related deaths respectively. Identification of the symptoms of NAFLD patients is diverse, given the associated poorer results. In order to target people who are suffering from NAFLD, many non-invasive tools have been developed that can provide an update on the epidemiology, clinical and prognostic features, and diagnostic approach to patients with NAFLD and NASH.
Although NASH or NAFLD develops without vigorous symptoms, we can always take small steps towards a healthier lifestyle to prevent the fat from accumulating in liver. Taking such steps can heal us from fatty liver disease and give us a healthy liver which in turn reflects in the overall health.
