The management of NAFLD includes both treating the liver condition as well as the other associated or underlying metabolic disorders like insulin resistance, Type 2 diabetes, obesity and high fat levels in the blood.
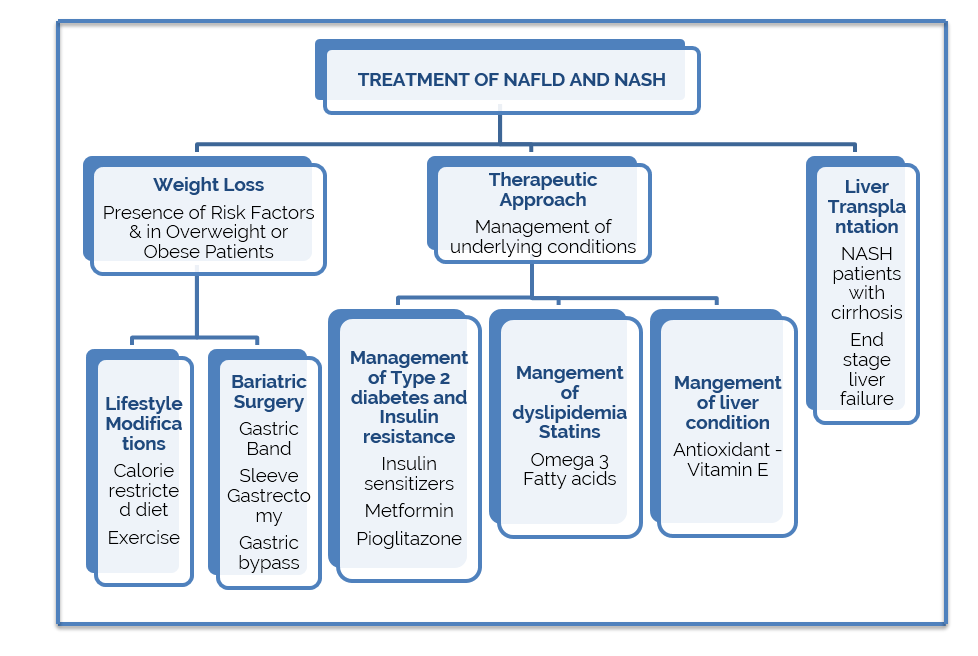
Management of NAFLD & NASH
NAFLD
Management of NAFLD
Lifestyle Modification for Weight Reduction
The main goal of management of NAFLD is weight loss. Lifestyle modification includes
- Modification of diet
- Physical activity – Exercise
Proven Benefits of Weight Loss in NAFLD and NASH patients
- Losing at least 10% of total body weight over a period can reverse NAFLD and improves NASH
- Losing ≥5% body weight stabilized or improved fibrosis
- Prevents NAFLD progression to more serious forms like fibrosis and NASH
- Reverses the NAFLD – simple fatty liver
- Improved outcomes that are proportionate to improvement in liver condition in NASH patients
Diet Modification
Dietary modifications with calorie-restricted diet are recommended in patients who are over weight or obese to reduce weight and to improve metabolic disorders.
What is a Calorie-Restricted Diet?
Daily diet should be calorie deficient for example if a person needs total 2000 calories in day according to his BMI (proportion of weight to height) to sustain day-to-day activities or to maintain weight, the person should consume less than that.

Advantages of calorie-restricted diet in NAFLD and NASH patients
Following a calorie restricted diet over a period will result in
- Weight loss
- Associated with mobilization of fat accumulated in the liver
- Improves other associated metabolic disorders
Which is the recommended calorie-restricted diet?
There is no particular diet with particular proportions of macronutrients (carbs, proteins, fats) recommended for weight loss at present. But Mediterranean diet consisting of high amounts of fresh fruits, vegetables, olive oil and low amounts of protein is found to be beneficial in improving the fat content in the liver.


Exercise
Along with calorie restricted it advised to indulge in physical activity like walking, jogging, swimming and cycling to assist in weight loss and to improve metabolic disorders.
What should be the duration and intensity of exercise?
There is no recommended duration and intensity of exercise. But studies have shown that those who maintain a physical activity for more than 150 minutes per week and increase it every week have shown to improve their liver enzymes (ALT and AST) and metabolic disorders regardless of weight loss.


No alcohol consumption
Patients with NAFLD are recommended not to take any alcohol of any type or amount.
Therapeutic Approach
Management with medicines is preserved only for NAFLD patients
- Diagnosed with NASH by biopsy
- Presence of risk factors for NASH
- Presence of fibrosis
- To treat the underlying metabolic disorders, liver disease
To prevent outcomes of NAFLD or NASH in the long-term
Management of Insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes with Insulin Sensitizers
These are a group of drugs that are aimed at treating insulin resistance and other metabolic disorders associated with glucose and fat metabolism
- Metformin: Metformin is recommended only in NAFLD patients who are insulin resistant and Type 2 diabetic but not to treat NASH.
- Thiazolidinediones: Among Thiazolidinediones, pioglitazone is found to improve liver condition in NASH patients with and without diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity, liver enzymes and fat content in the liver
Management of Dyslipidemia with Statins
Patients with NAFLD have dyslipidemia a condition with high triglycerides and abnormal fat levels in blood that can contribute to worsening of NAFLD and increased heart risk. Dyslipidemia in NAFLD patients is treated with a category of drugs called statins that reduce the abnormal fat levels in blood and improve the elevated liver enzymes and reduce heart risks.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are not specifically recommended to treat NAFLD or NASH but are considered to treat hypertriglyceridemia (high levels of triglycerides) in patients with NAFLD.
Management of Liver condition with Vitamin E (rrr α – tocopherol)
Vitamin E is considered as an anti-oxidant and its administration has shown to improve liver conditions like elevated liver enzymes, fat accumulation, cell death and inflammation of liver in NASH patients without Type 2 diabetes. Risks and benefits are assessed carefully before starting the treatment with Vitamin E. It is to be noted that Vitamin E is not recommended in NAFLD patients without biopsy, NASH patients with diabetes and NASH cirrhosis or cryptogenic cirrhosis.
Surgical Approach
Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery is a type of surgery done to reduce weight by reducing the capacity of food intake.
Various types of bariatric surgery used for weight loss
- Gastric band
- Sleeve gastrectomy
- Gastric bypass
Bariatric surgery is recommended in
- Heavily obese and overweight patients with risk factors
- Patients who can not lose by physical exercise and calorie restricted diet due to weight and other co-existing disease conditions
Advantages of bariatric surgery in NAFLD and NASH patients
- Reduction of weight
- Improve NAFLD, and associated metabolic disorders
- Improves long-term survival and reduce the heart related disorders
Liver Transplantation
Liver transplantation is done only in
- NASH patients with cirrhosis
- End stage liver failure
Considerations for Liver transplantation
Lot of factors like obesity and other associated risk factors like heart and kidney complications are thoroughly studied before the surgery. As most of the NASH patients are severely obese, weight loss through diet and exercise are recommended before the surgery and are recommended to maintain weight after the surgery for improved and sustained outcomes.
Reference:
Chalasani, N. , Younossi, Z. , Lavine, J. E., Charlton, M. , Cusi, K. , Rinella, M. , Harrison, S. A., Brunt, E. M. and Sanyal, A. J. (2018), The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology, 67: 328-357. doi:10.1002/hep.29367
